The Ordinance for Partial Revision of the Enforcement Regulations of the Food Sanitation Law (Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare, Japan Ordinance No. 163, 2012) and revisions to some of the standards for foods and additives (Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare, Japan Notification No. 595, 2012) were promulgated, along with the revision of the Enforcement Regulations of the Food Sanitation Law and the standards for foods and additives.
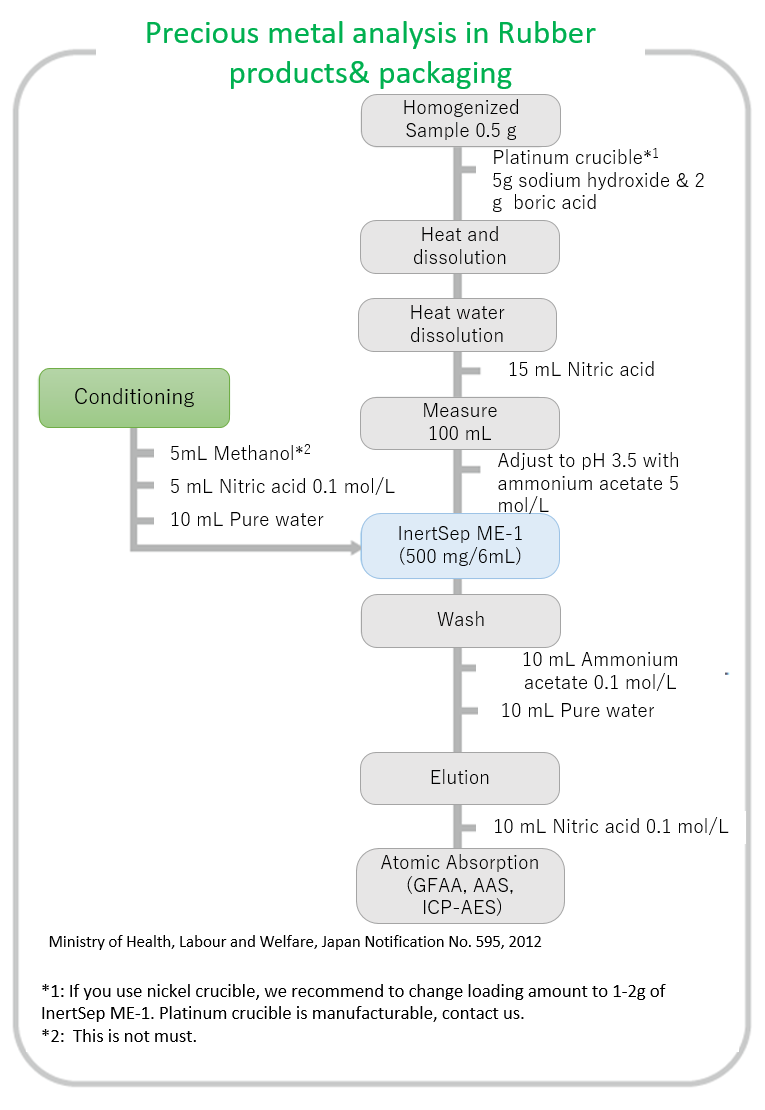
In the partial revision, the alkali melting method was applied to the test of cadmium and lead in rubber equipment or containers and packaging. The test method for cadmium and lead in rubber-made nursing bottles using this test method is also mentioned.
The demand for metal analysis is increasing in the food industry. One of these is the analysis of heavy metals in containers and packaging. The Food Sanitation Law specifies testing methods for the measurement of cadmium and lead in rubber equipment and containers and packaging. The second is the analysis of trace mineral components as dietary ingredients. Microwave decomposition equipment is convenient for analyzing trace elements in crops, where different samples can be rapidly and automatically disassembled. Conventional decomposition methods using hot plates, beakers have been developed using a simple automatic decomposition system that uses heat blocks to shorten the analysis time.
Measurement of Precious Metals in Rubber Containers and Packaging
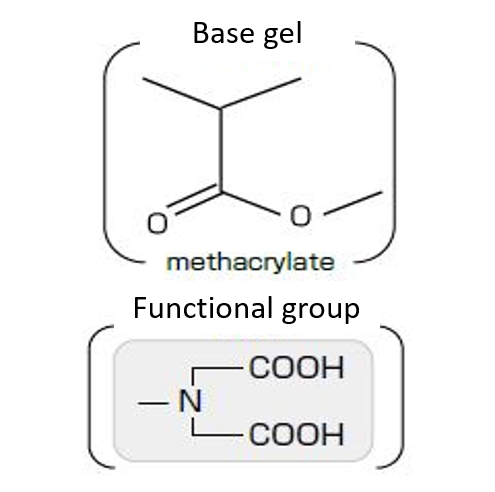
InertSep ME-1
InertSep ME-1 is a minicolumn based on a polymer of methacrylate and incorporates an iminodiacetic acid-type chelating functional group. It is suitable for selectively concentrating more than divalent metal cations, because it is highly hydrophilic and does not retain monovalent Na and K ions.