Basics of Gas Chromatography
2-1 Overview of Capillary Columns
A capillary column is a hollow narrow tube coated or chemically bonded with a liquid phase or adsorbent on its inner surface. The typical capillary column material is silica tubing. Fused silica is popular because it is highly pure and has a low surface active point (metal content ≤ 1 ppm, OH group content < 120 ppm). The outer surface of the tube is coated with polyimide resin, which renders it robust against breakage and easy to handle.
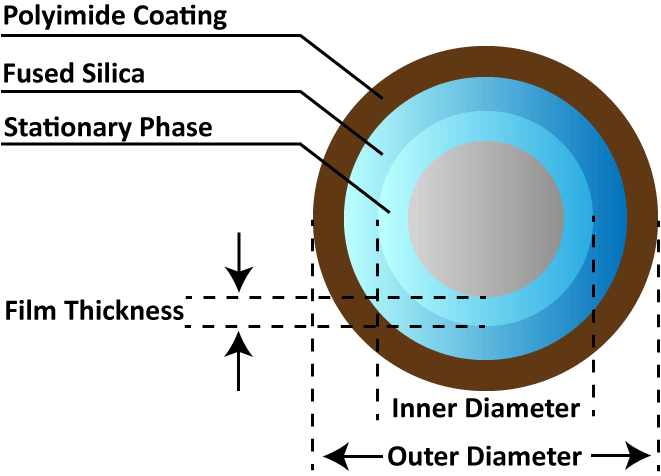
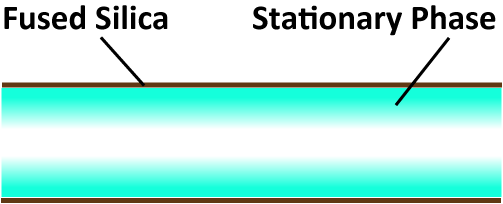
WCOT
Capillary columns are broadly classified into three types: the wall-coated open tubular (WCOT) type, the support-coated open tubular (SCOT) type, and the porous-layer open tubular (PLOT) type. The internal capillary tube of the WCOT type is coated or chemically bonded with a liquid phase. In the SCOT type, the carrier is impregnated with the liquid phase and fixed to the inner wall. Meanwhile, the PLOT type uses a porous polymer, alumina, or molecular sieve. Today, the most widely used capillary columns are chemically bonded WCOT types. In this chemically bonded capillary column, after the liquid phase is applied to the inside of the capillary tube, the liquid phases are chemically bonded to each other or the liquid phase is chemically bonded to the inner surface of the capillary.